
Choose posture analysis and upload a photo or take a picture from your subject.
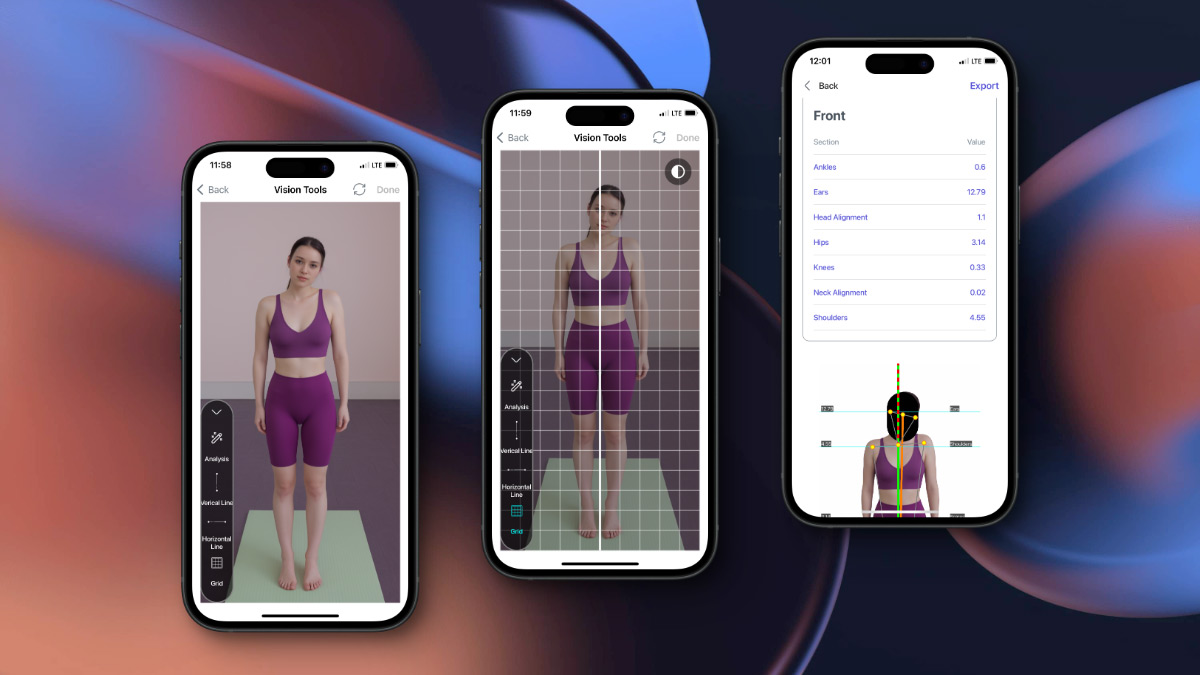
Select the analysis and see results about alignment between knees, ankles, hips, shoulders and ears.
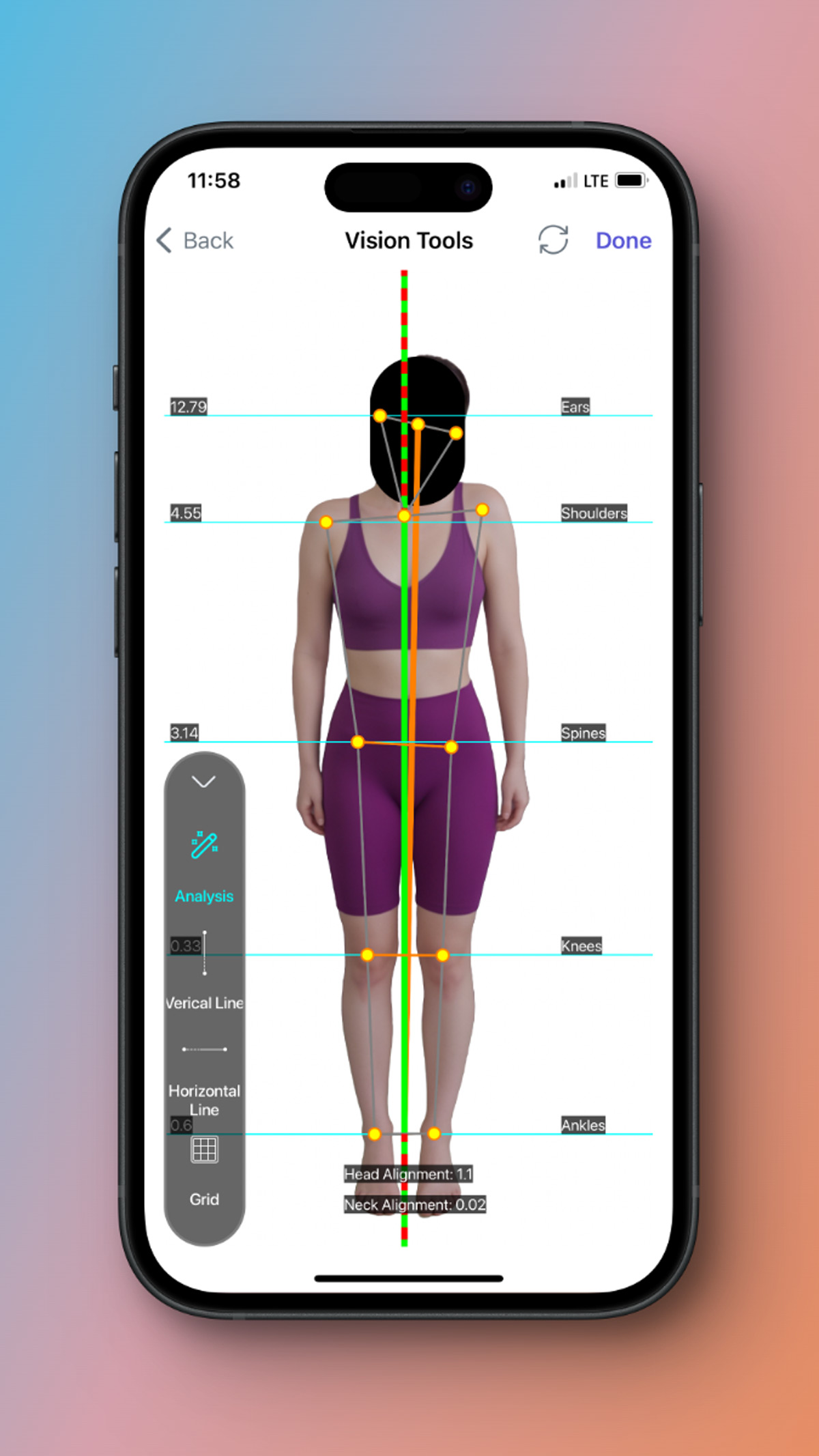
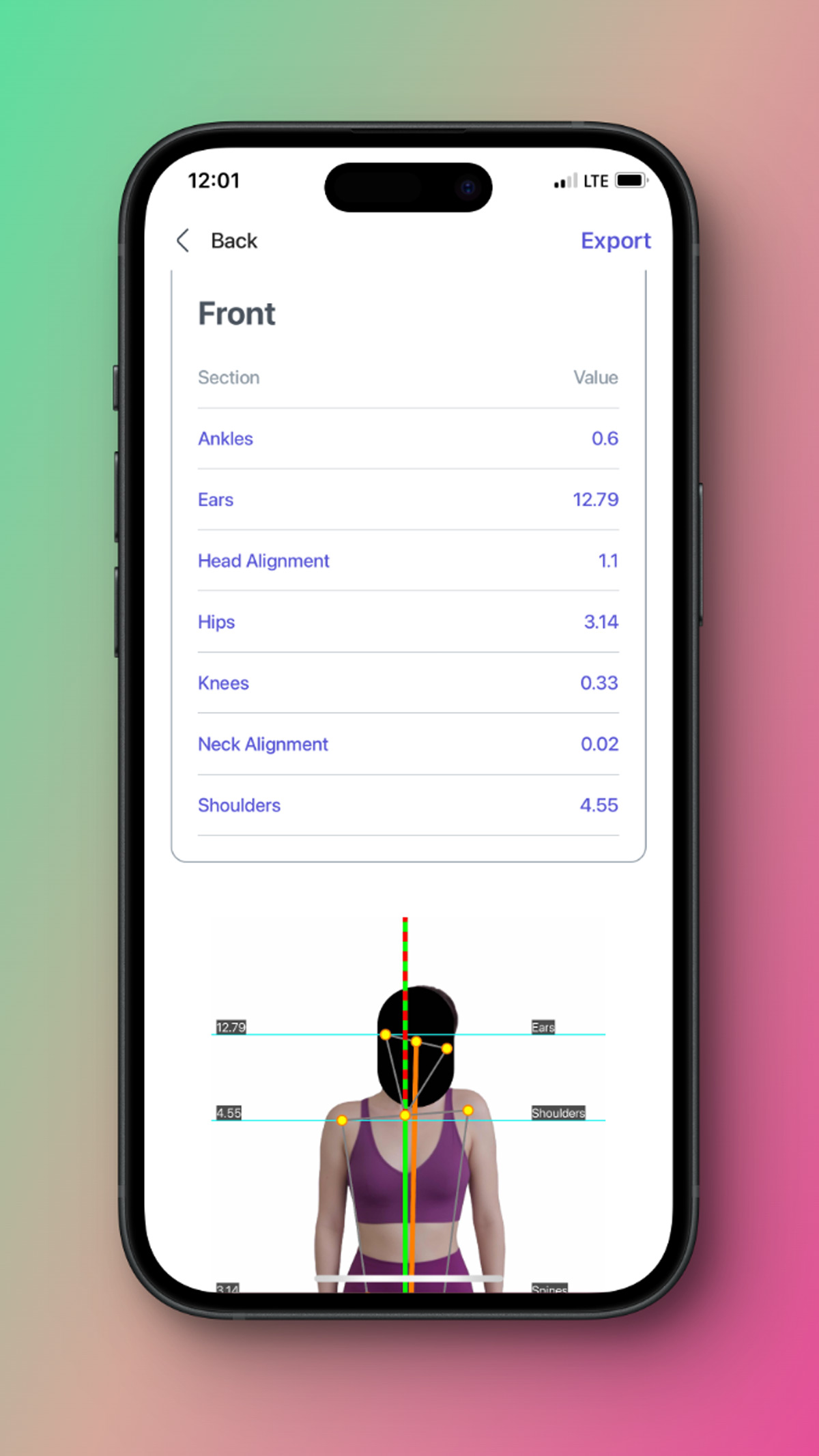
It's a result of detection and you can assign to your subject's profile and save it and if you want can share it with any social media.
For more detail you can use horizontal lines on ears and eye s and see alignments.
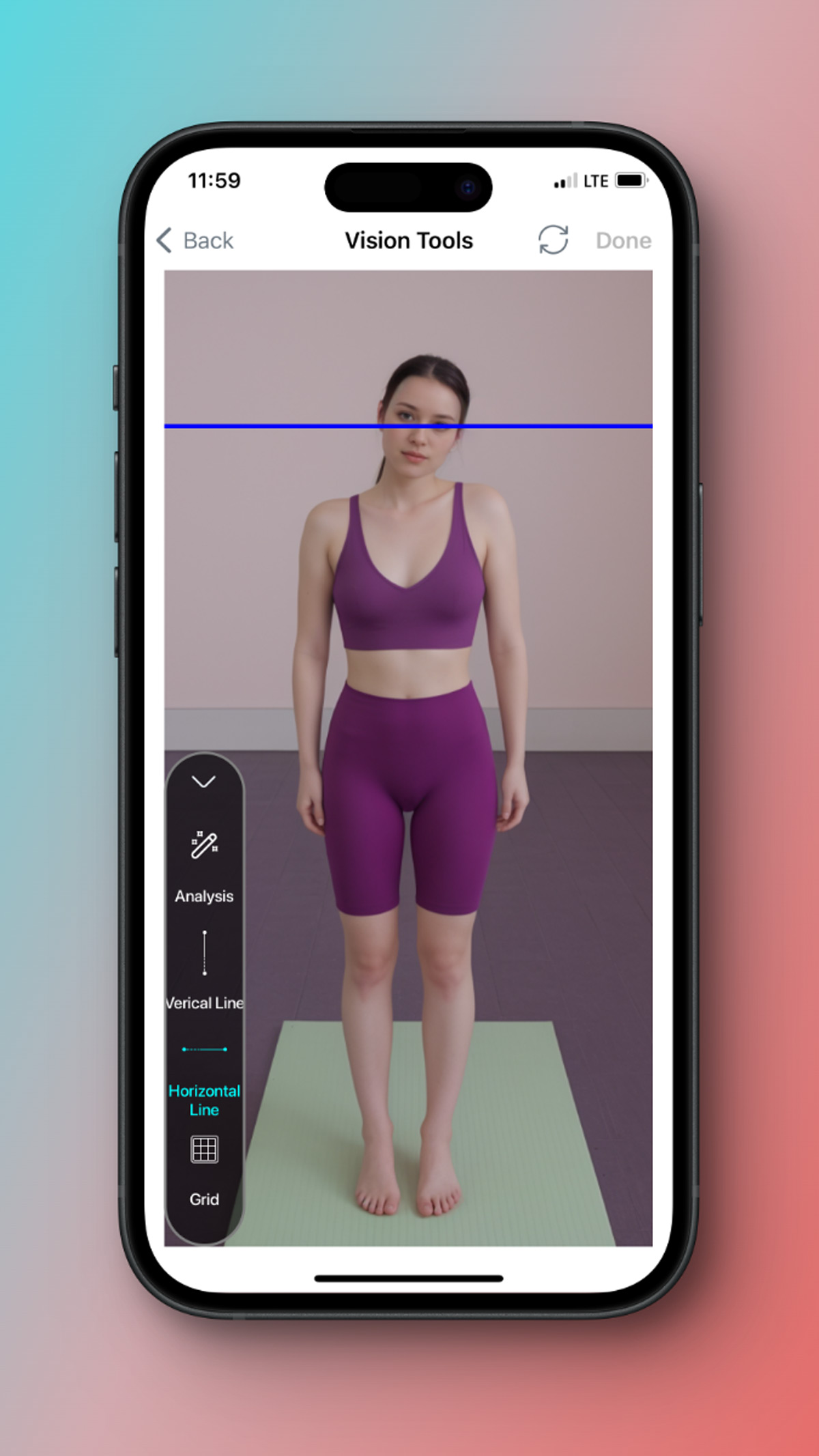
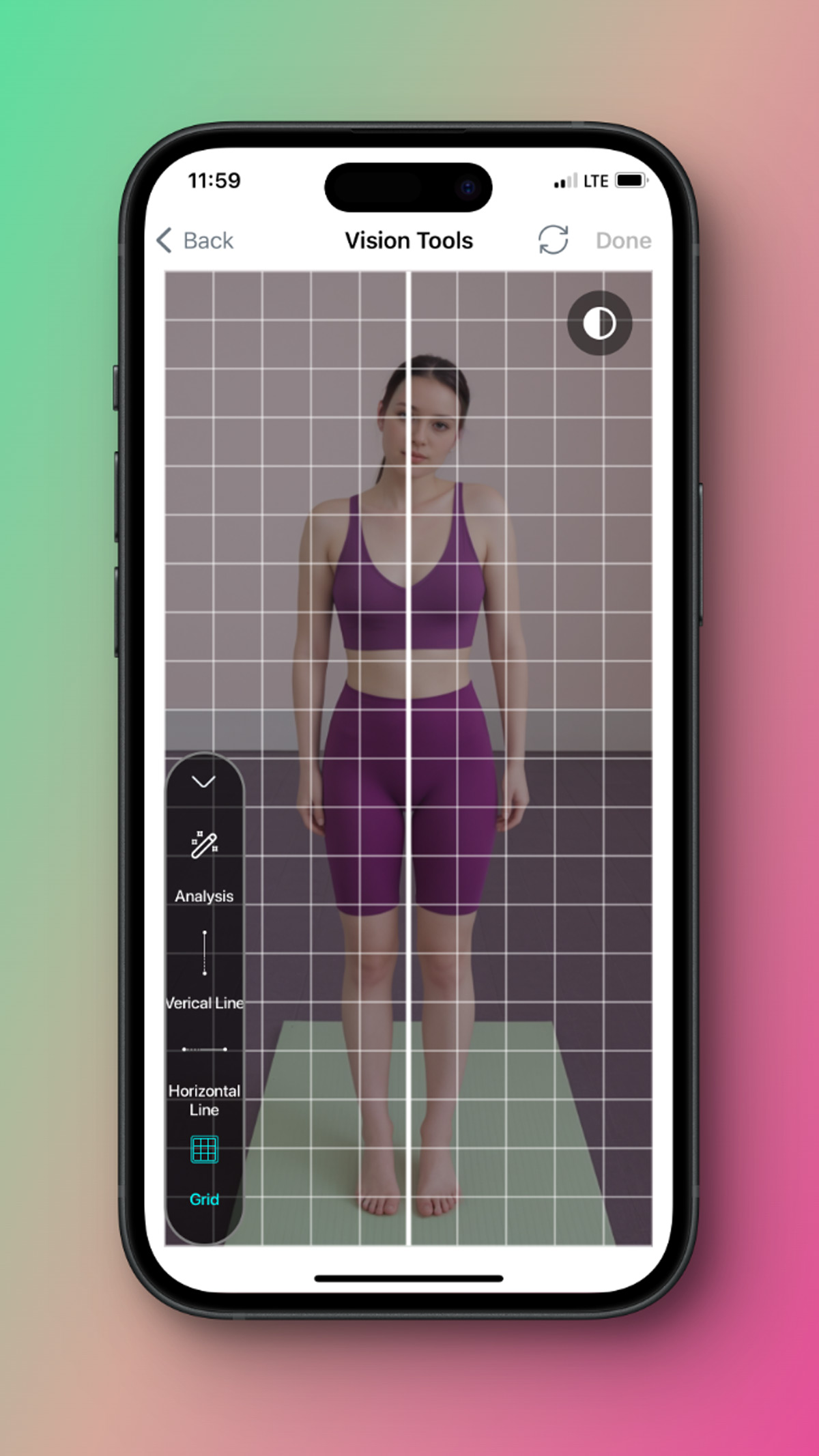
Last option it's a grid and when you choose it you can see better visual assessment.
Torticollis Therapy: Enhancing Recovery Process
1.Manual Therapy and Mobilization:
• Implement techniques like cervical mobilizations, soft tissue massage, and myofascial
release to alleviate joint restrictions and muscle tightness.
2.Targeted Exercise Therapy:
• Focus on stretching and strengthening exercises for the cervical muscles to promote
balanced muscle development and improve range of motion.
• Include sensorimotor and proprioceptive training, particularly useful in cases of
dystonic torticollis, to bolster neuromuscular control.
3.Neuromuscular Re-education and Ergonomic Training:
• Apply strategies to enhance postural awareness and correct detrimental postural
habits.
• Make ergonomic adjustments in daily routines to lessen strain on the cervical spine,
particularly important for clients spending long periods at a desk or performing repetitive movements.
• Coaching Approach: Develop an intensive, multifaceted rehabilitation program. Focus on
advanced strengthening, and neuromuscular retraining, including proprioceptive and balance exercises.
Collaborate with healthcare professionals for a multidisciplinary approach.
Critical Sway Back:
• Characteristics: Extreme postural deviation with significant functional
limitations.
• Biomechanical Implications: Profound alterations in spinal and pelvic biomechanics,
potentially affecting overall movement efficiency and systemic health.
After assessment , you can record the process of treatment and improvement in the corrective movement of the
person.
Conclusion:
Torticollis, or wry neck, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical head or neck position, which can
be congenital or acquired. It typically involves an overactive or shortened sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
muscle, causing the head to tilt towards and the chin to rotate away from the affected side. The atypical
head and neck positioning can result in compensatory shifts in cervical spine alignment, influencing overall
spinal posture and balance. Spasmodic torticollis or cervical dystonia involves neurological factors that
cause involuntary muscle contractions and posture issues. There are different types of torticollis in
adults, based on severity, duration, and causes, and it's essential to adapt training and provide
appropriate support accordingly. Advanced assessment tools, such as the flexitrace application, can help
identify alignment issues and provide a visual analysis. Incorporating therapeutic intervention strategies
for clients with torticollis can significantly enhance their training and recovery process, including manual
therapy and mobilization techniques, targeted exercise therapy, and neuromuscular re-education and ergonomic
training.