
You can upload a side picture or take it in the spine part and analyze the results.
In the result, you can see the difference between the pelvic line and ear line, which indicates whether the spines are healthy or not.
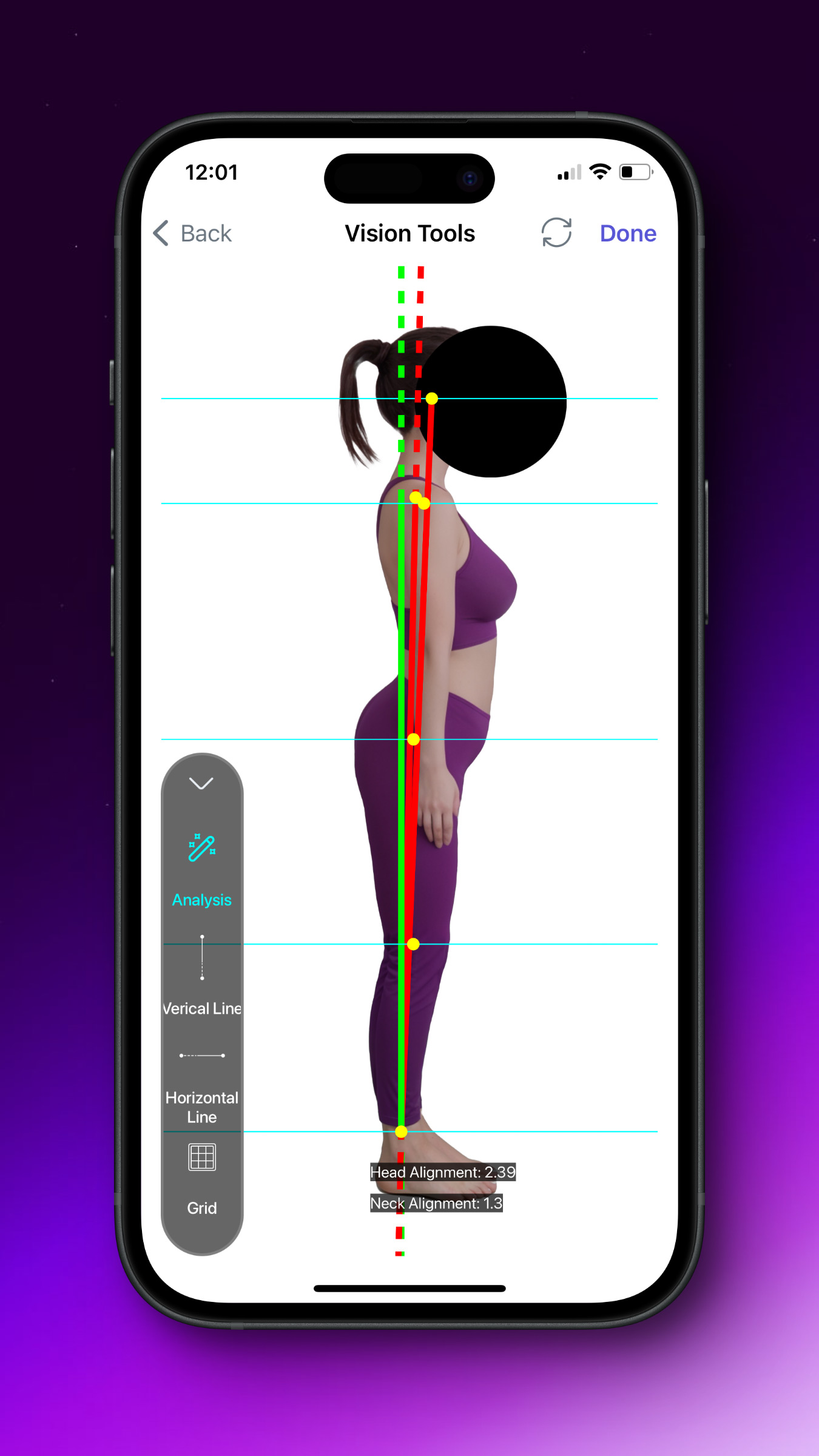
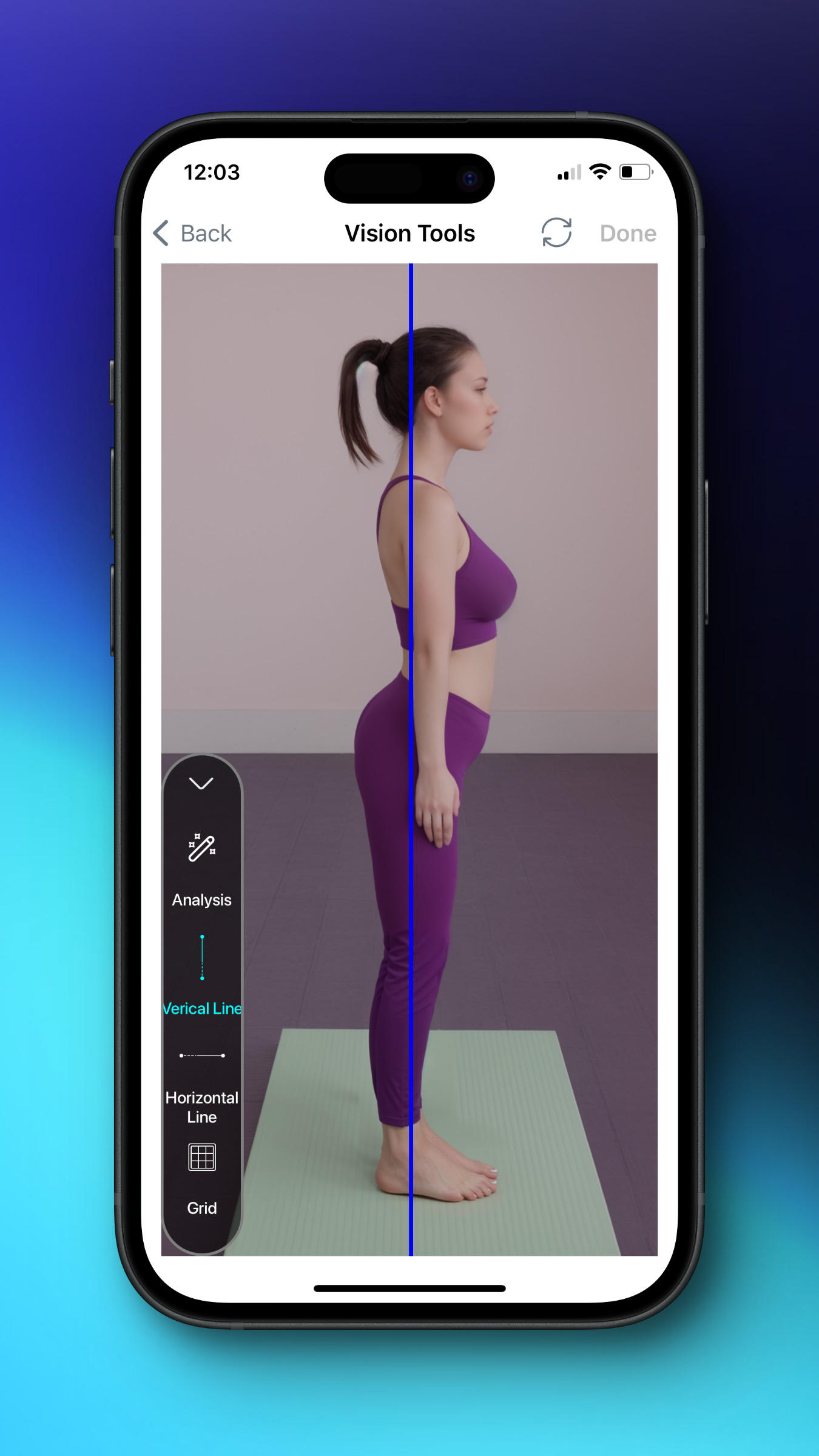
Alternatively, you can use two horizontal lines and a vertical line that you can put on the ankle, knee, and shoulder. If your subject has hyperlordosis, you can see that the pelvic has lateral tilt and the hip joint is out of the limited vertical line.
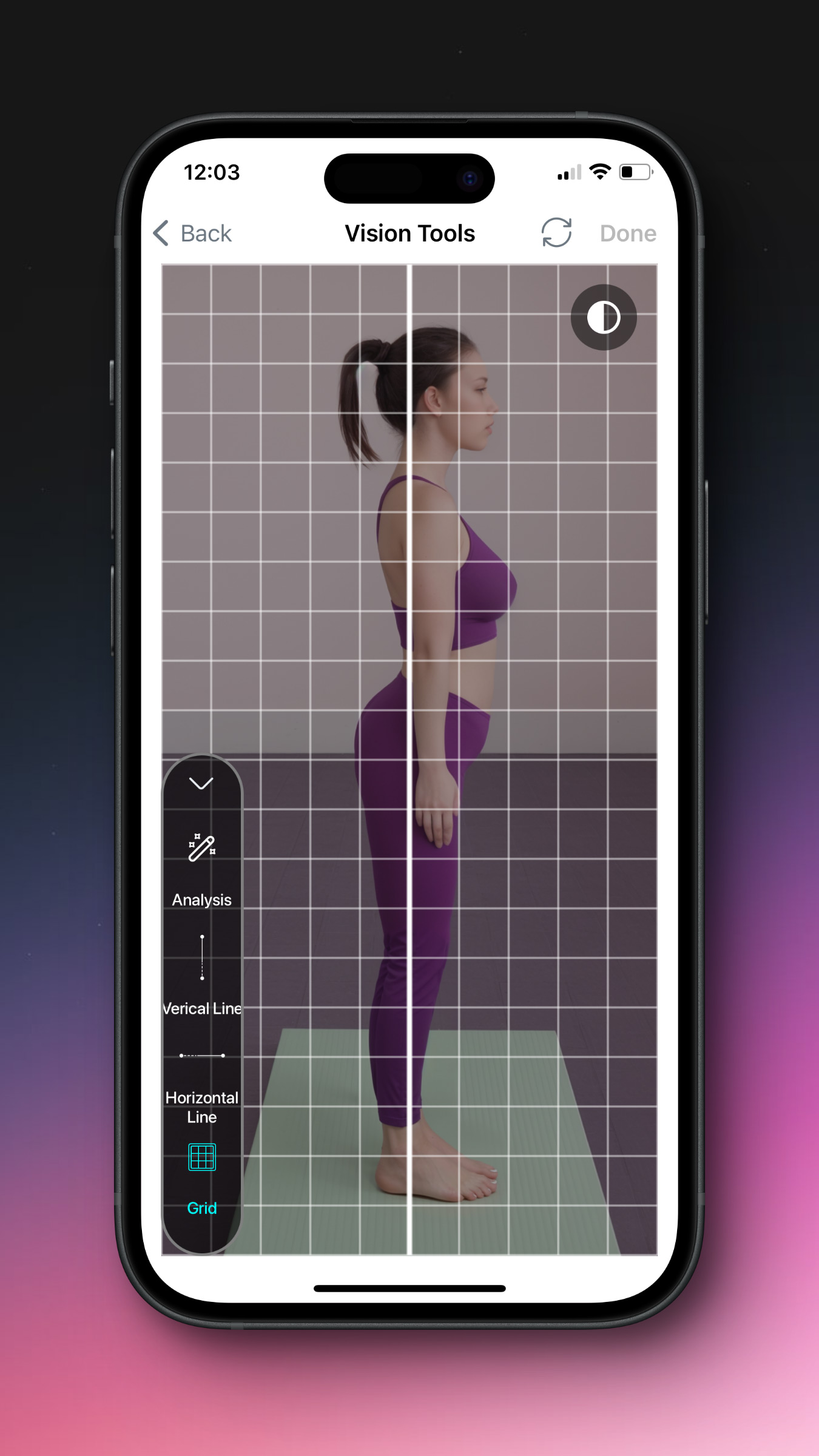
You can also use The grid for better assessment.
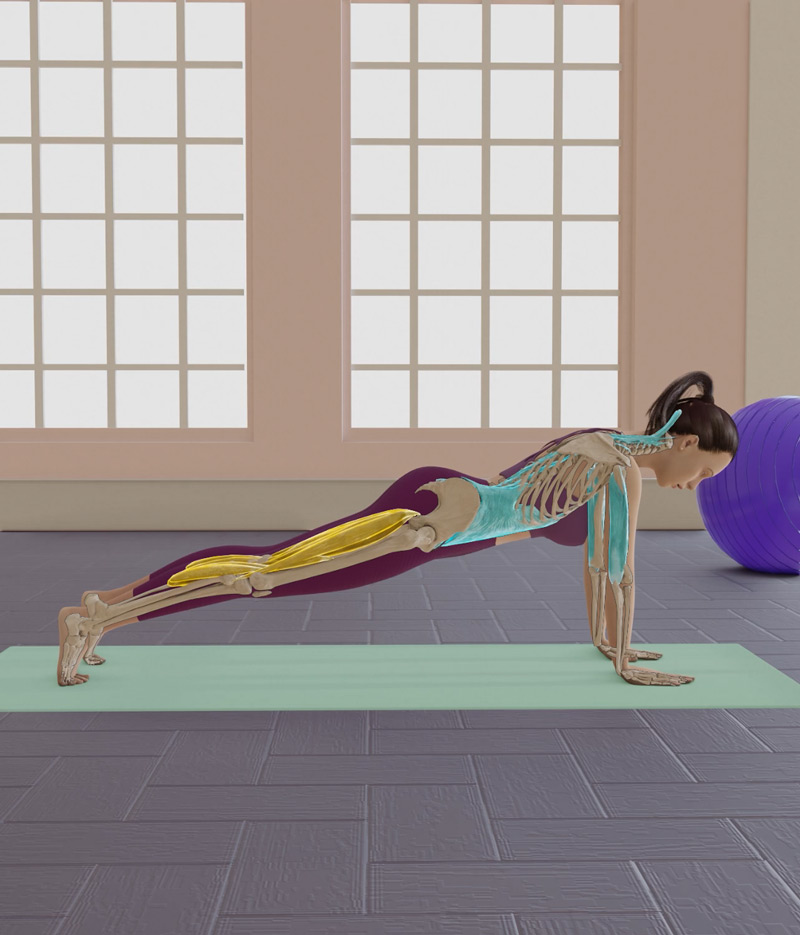

Engage core, back straight, arms locked, squeeze glutes and hold for 15-20 seconds..
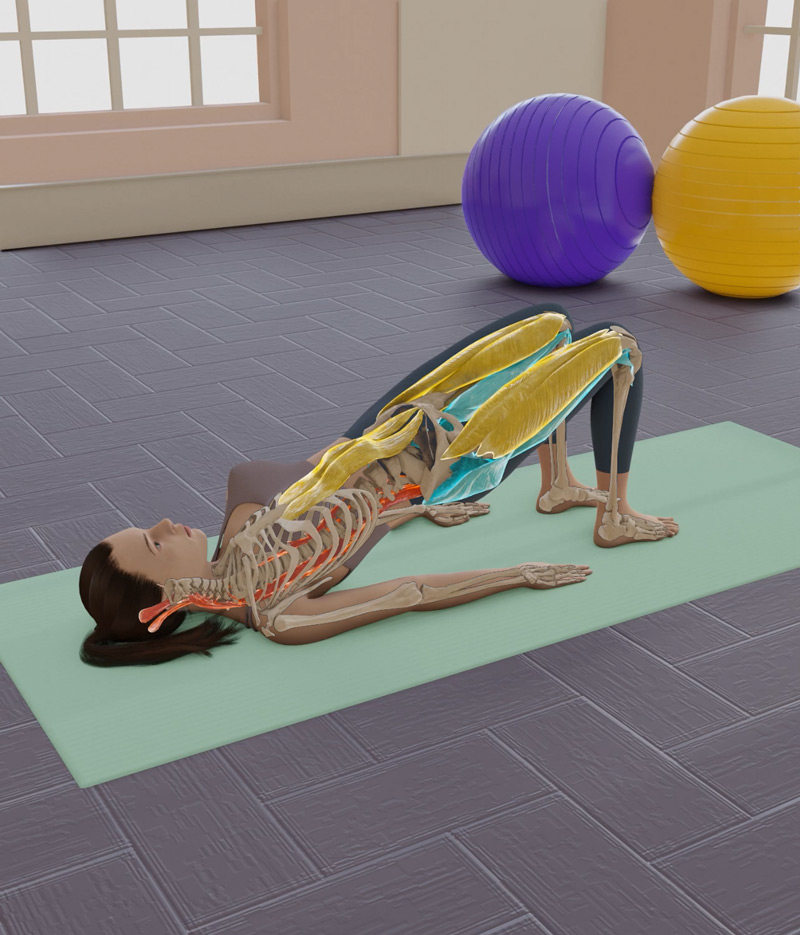

Lie down, knees bent, lift hips, squeeze shoulder blades, hold 15 seconds, repeat 10 times.
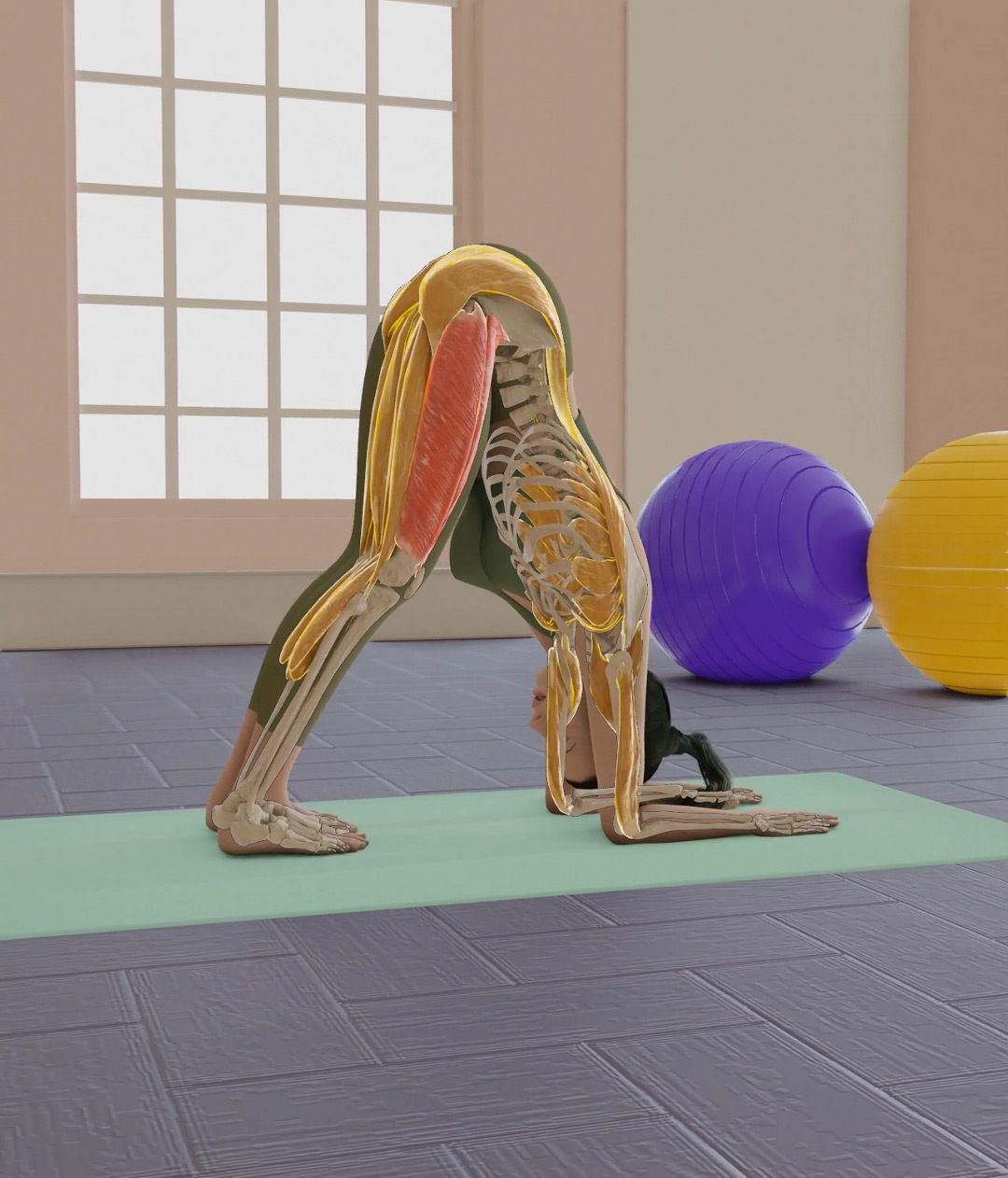

On forearms, tuck toes under, lift hips up, engage core, hold for 30-60 seconds.
Management of Hyperlordosis:
• Exercises: Focus on strengthening the abdominal muscles, coupled with stretching
exercises for the lower back and hip flexors.
• Activity Modifications: Avoid activities that can worsen the condition, such as wearing
high heels or prolonged standing without movement.
• Ergonomic Adjustments: Arrange work environments to promote and support good
posture.
Prevention Strategies:
• Regular Exercise: Engage in a balanced fitness regimen that encompasses both strength
training and flexibility exercises.
• Posture Awareness: Consistently be mindful of maintaining correct posture throughout
the day.
• Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to minimize back strain.
Conclusion:
hyperlordosis is a condition that fitness and bodybuilding coaches should be aware of, as it can
significantly impact a client's posture, muscle balance, and overall well-being. By focusing on spinal
balance and posture, muscular considerations, lifestyle impact, posture habits, weight management, and
genetic factors, coaches can help clients prevent and manage hyperlordosis. assessment
techniques, such as the flexitrace application, can aid in identifying the condition, while exercises,
activity modifications, and ergonomic adjustments can help manage it. Prevention strategies, including
regular exercise, posture awareness, and weight management, are essential for maintaining a healthy spine
and minimizing the risk of back pain and injury.